Components
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. Aenean massa. Cum sociis natoque penatibus et magnis dis parturient montes, nascetur ridiculus mus. Donec quam felis, ultricies nec, pellentesque eu, pretium quis, sem. Nulla consequat massa quis enim. Donec pede justo, fringilla vel, aliquet nec, vulputate eget, arcu. In enim justo, rhoncus ut, imperdiet a, venenatis vitae, justo. Nullam dictum felis eu pede mollis pretium. Integer tincidunt. Cras dapibus. Vivamus elementum semper nisi. Aenean vulputate eleifend tellus. Aenean leo ligula, porttitor eu, consequat vitae, eleifend ac, enim. Aliquam lorem ante, dapibus in, viverra quis, feugiat a, tellus.
- ONLY U.S. GRADE A DAIRIES
- WORLD'S LARGEST COLOSTRUM PRODUCTION CAPACITY
- 35+ YEARS EXPERIENCE
- A MISSION OF ETHICS
Let’s connect about colostrum
Are you a farmer looking for a partnership?
NUTRITIONAL ELEMENTS OF COLOSTRUM
NUTRITIONAL ELEMENTS OF COLOSTRUM
Growth and Repair Factors
Growth Factors: help stimulate cell growth, cellular differentiation and cell maturation. Growth factors act as signaling molecules from one cell to another as well as regulating a variety of cellular processes.
Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGF-I and IGF-II)
The most abundant growth factors of bovine colostrum. These proteins are single chain polypeptides with amino acids. They play an important role in childhood growth and have an anabolic effect in adults.
- Primary structures are highly conserved across species and have identical sequences in humans17
- Heat and acid stable and widely distributed mediators of cell growth, development, and differentiation18
- Amino acid sequence of purified bovine IGF-I is identical to that of human IGF-I19,20
- Dietary IGF-I can stimulate cell proliferation in the gastrointestinal tract21,22
- Dietary IGFs may have a direct effect on the epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract and can be absorbed into circulation23
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)
Plays an important role in the regulation of cell growth, proliferation and differentiation. The EGF family of growth factors can help modulate development of the epidermis, mammary gland, and gut.
- Stimulates the repair process at the site of inflammation24
- Plays an important role in preventing bacterial translocation and stimulating gut immunity25,26
- Anabolic growth factor with possible differentiation-inducing factors for intestinal epithelium of newborns, suggesting possible applications of recombinant IGF and IGF analogs for repair of damaged gastrointestinal tissues27
- Supplementation with EGF may aid in the recovery of traumatized gastric and intestinal tissues28
Broad Spectrum Antimicrobials
Lactoferrin
Iron-binding glycoprotein. One of the antimicrobial components of the immune system that fights bacteria and fungi in the body. It binds metal ions which are necessary bacterial metabolites, making them unavailable for bacterial development. This anti-inflammatory glycoprotein binds free iron ions in biological fluids, transporting the iron to blood cells. Lactoferrin has been shown to inhibit the growth of specific microbes, like E. coli and Salmonella. Lactoferrin has additionally demonstrated antiviral effects.
- Lactoferrin is an 80 kDa iron-binding glycoprotein with antiviral and antimicrobial activity
- Shown to inhibit the growth of specific microbes including Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella, dysenteria, and Streptococcus mutans6,7,8
- Antiviral effects against herpes simplex virus type-1 (HSV-1), human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) and human cytomegalovirus9,10
- Plays an important role in iron uptake in the intestine and in the activation of phagocytes and immune responses3
- Immune mediator regulating target cells responses, including those involved in oxidative stress and systematic inflammatory responses
- Clinical studies show lactoferrin can inactivate LPS and inhibit dermal inflammatory cytokine production, indicating lactoferrin may have a potent anti-inflammatory effect11
Lyzozyme
Antibacterial enzymes that help to support the immune system by disrupting the cell walls of harmful bacteria. A special attribute of lysozyme is its interaction with other colostral components. It has been shown to work in a synergistic effect with lactoperoxidase, IgA and lactoferrin. With lactoperoxidase, lysozyme partly activates it by forming a complex. With IgA, it works in synergy to combat E. coli. And in the presence of lactoferrin, the antimicrobial effects of lysozyme are also enhanced.
- An enzyme that helps to support immune function by attacking specific bacteria and fungi
- Lysozyme interacts with other components in colostrum, like lactoperoxidase, lactoferrin and IgA, resulting in a synergistic blend of antimicrobials3
- The natural substrate of this enzyme is the peptidoglycan layer of the bacterial cell wall and its degradation results in the lysis (breaking down of the cell wall) of the bacteria12
Pre-Headline
Headline
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Aenean commodo ligula eget dolor. Aenean massa. Cum sociis natoque penatibus et magnis dis parturient montes, nascetur ridiculus mus. Donec quam felis, ultricies nec, pellentesque eu, pretium quis, sem. Nulla consequat massa quis enim. Donec pede justo, fringilla vel, aliquet nec, vulputate eget, arcu. In enim justo, rhoncus ut, imperdiet a, venenatis vitae, justo.
Immune Factors
Immunoglobulins
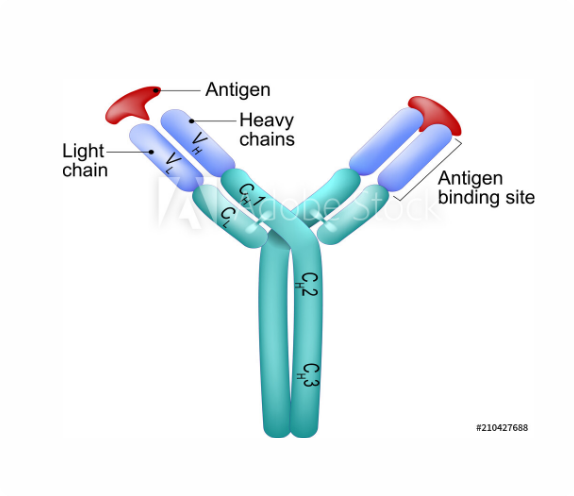
Colostrum contains IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE1
-
IMMUNOGLOBINS (Ig)
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Dolor, quo.
-
IgG
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Dolor, quo.
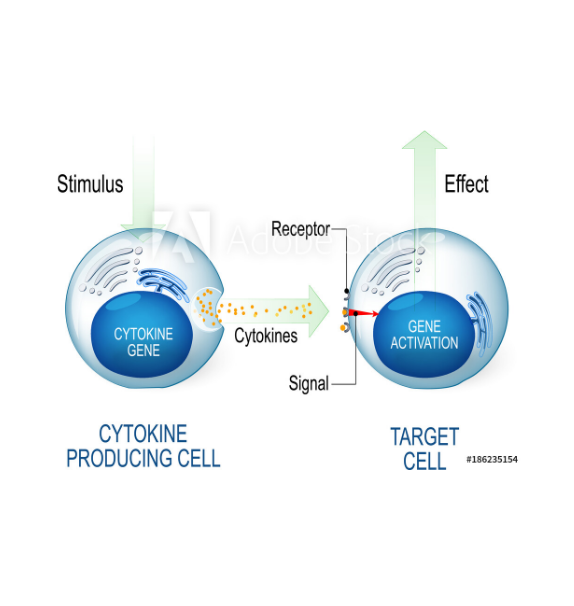
Cytokines
Colostrum contains many of these biological response modifiers. These can be protein, peptide or glycoprotein signaling molecules that are used in cellular communications. Cytokines have a specific role as regulators of epithelial cell growth and development, including intestinal inflammation and epithelial restoration following mucosal damage. They are also important mediators in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses.
- Colostrum contains numerous cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-1ra2
- These small peptide molecules are important mediators in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses3
- In the newborn, cytokines play an important role in combination with the ingested maternal immunoglobulins and non-specific antibacterial components of colostrum4
- They are major regulators of epithelial cell growth and development, including intestinal inflammation and epithelial restitution following mucosal damage
Cytokines
Colostrum contains many of these biological response modifiers. These can be protein, peptide or glycoprotein signaling molecules that are used in cellular communications. Cytokines have a specific role as regulators of epithelial cell growth and development, including intestinal inflammation and epithelial restoration following mucosal damage
Cytokines
Colostrum contains many of these biological response modifiers. These can be protein, peptide or glycoprotein signaling molecules that are used in cellular communications. Cytokines have a specific role as regulators of epithelial cell growth and development, including intestinal inflammation and epithelial restoration following mucosal damage.


